

Abstract:
In this article, the author explores the integration of XIPU AI into the creation of online quizzes to support the teaching and learning of a degree preparation module in an English Medium of Instruction (EMI) program. The rationale behind the use of AI includes supporting content and language learning, accelerating material development and enhancing efficiency. Building upon the ADDIE model and the LLM functions, it introduces a 7-stage procedure involved in the quiz creation. While AI technology can offer valuable support in language learning to meet pedagogical goals and enhance students’ learning experiences within EMI programs, the author emphasizes the importance of a collaborative approach between AI and human expertise, which calls for teacher involvement to ensure the accuracy and reliability of AI-generated materials.
Introduction
Here at XJTLU, the English Medium of Instruction (EMI) programs are offered to university students, along with concurrent language support to ensure that students are equipped with the necessary language skills to succeed in their degree preparation modules. While supporting the module “Trend in Marketing and Information Management” in the second semester for freshmen, the author of this article explored the innovative practice of integrating AI into the creation of online quizzes. This article will briefly explain the rationale behind the integration, outline the procedures involved in this practice, and provide a few examples of the quizzes assisted by AI, and reflect on the challenges and limitations as well as the critical roles for teachers to play in this process.
The AI Integration Practice
The rationale behind integrating AI into the quiz creation process is multi-faceted. Firstly, the quizzes serve to create weekly post-lecture activities that cover both conceptual understanding (Paturusi, Chisaki, and Usagawa, 2014) and language aspects. These quizzes aim to provide practice and review components for the students, as highlighted by Cohen and Sasson (2016). Secondly, there has been an extensive utilization of AI for EFL material and assessment development since AI technologies were introduced to the language education field. Large Language Models, particularly Chat GPT, have the potential to streamline and accelerate material development (Koraishi, 2023), and enhance the assessment creation process for educators. Thirdly, the integration of AI into quiz creation improved the overall work efficiency for EFL teachers who have difficulty in becoming proficient in both subject matter and language exceeding the capabilities of their existing experience (Hutchinson and Waters, 1987, cited in Luo and Garner, 2017) when providing language support to subject modules.
Before touching upon the specific procedures of this AI-assisted quiz creation practice, it is important to be clear about the assessment development stages and the relevant AI functions. According to the relevant literature, the assessment development procedures should follow the stages of the ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation) model (Slamet & Mukminatien, 2024). When discussing the specific functions of large language models during the AI-assisted quiz creation processes, the AI is first utilized to analyze the course content materials (Owan, et. al., 2023) and extract relevant information (Özdere, 2023). Then it would help convert course content into quiz items that are precise, explicit and unambiguous, such as multiple-choice questions, true or false statements, and matching exercises (Owan, et. al., 2023). Subsequently, the most relevant and appropriate test items are identified and assembled from pool of quiz items generated by AI (Owan, et. al., 2023).
In this particular case, from an EAP lecturer’s perspective, the AI-assisted quiz creation procedures involve a thorough process (see Flowchart 1 below), including studying weekly lecture PowerPoint slides, noting down key terms and definitions in Excel documents, identifying potential linguistic difficulties, and planning language support aspects such as synonyms and paraphrasing. Prompts are written to request AI generation, followed by the evaluation of AI-generated quiz items and proofreading of answers. Finally, the quiz items are formatted before they are imported into the question bank on the Learning Management System, which is the quiz platform on LearningMall at XJTLU.
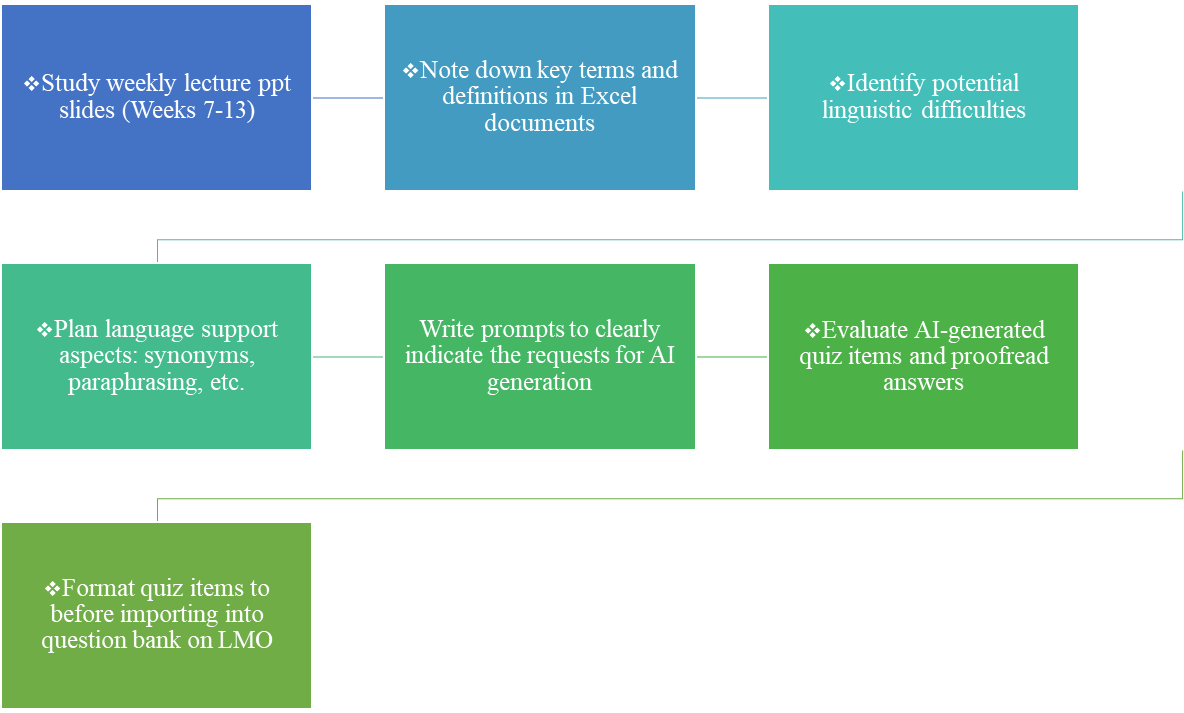
(Flowchart 1: Brief description of the AI-assisted quiz creation procedures)
In Table 1 below, the procedures for integrating AI throughout the processes are explained. When studying the weekly lecture contents, the author of this article quickly skimmed through the slides to search for the intended learning outcomes for each lecture, the definitions of the key terms, and corresponding examples. Extractions of these information could be done by manually copying and pasting the relevant sentences from the given slides or by sending requests to AI after the slides were uploaded to the AI knowledge base platform.
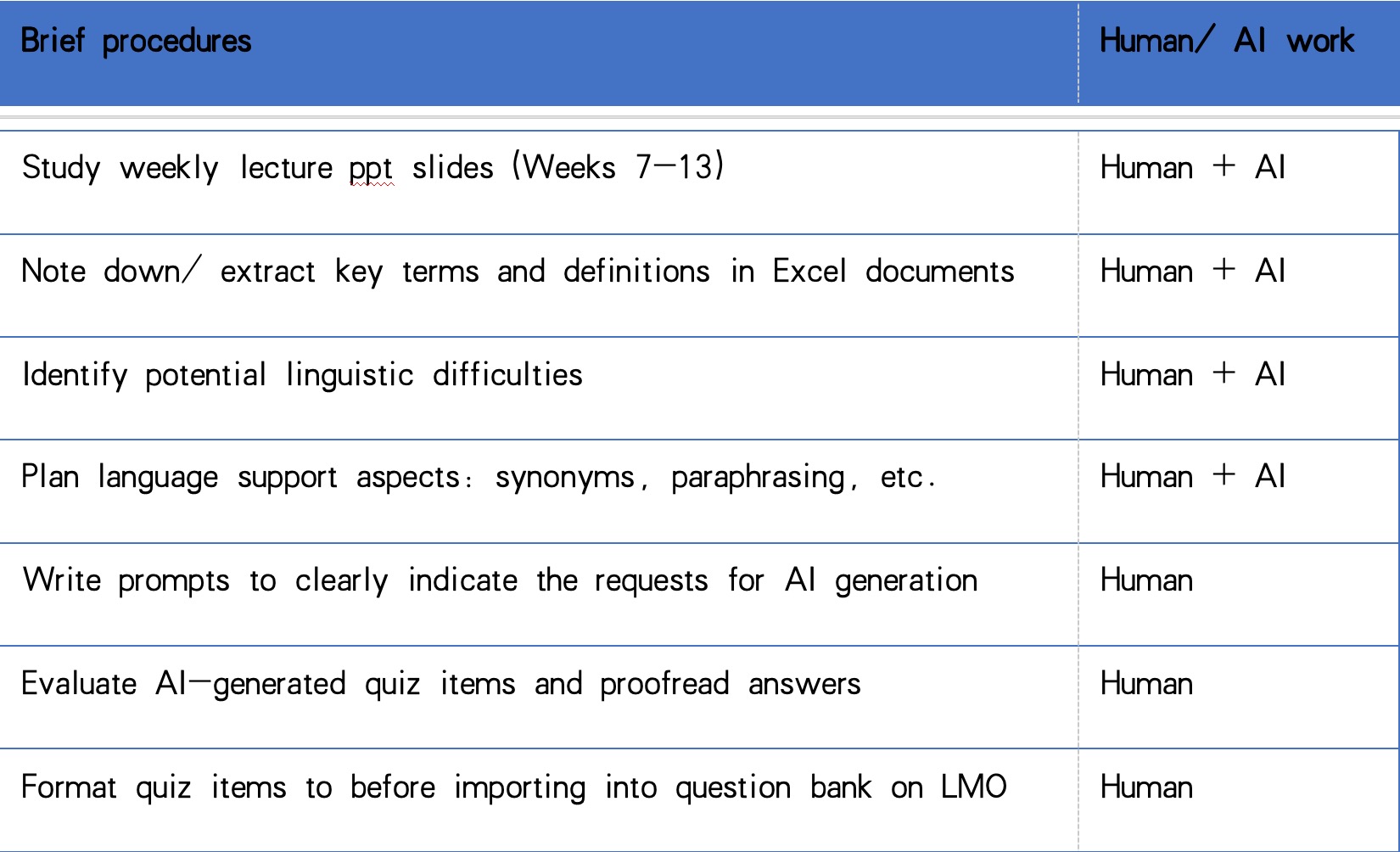
(Table 1: Brief description of the procedures and the AI V.S. human integration)
Subsequently, AI was requested to make a list of key vocabulary and sentences, and to categorize the words and sentences according to the CEFR levels, which provided valuable reference to the author in making decisions about which linguistic items to focus on. Once the potential linguistic difficulties or demands were successfully identified, clear prompts (see figure 1 below) were drafted to express requests detailing the quiz question types (see Figure 2 & 3 below), difficulty levels, cognitive domains of the questions, quiz answers and explanations, etc.

(Figure 1: Screenshot of an AI prompt)

(Figure 2: Screenshot of a Vocabulary question)

(Figure 3: Screenshot of a sentence paraphrasing question)
After receiving the AI generated texts, the author started proofreading the questions and answers to ensure the accuracy of the quiz items and make necessary adjustments or revisions. When the quiz items were found not as satisfactory as expected, further dialogues between the author and AI were carried out to gather more responses until more satisfying results were obtained. Once the quiz items were finalized, the author examined the quiz formats to ensure the quizzes can be successfully imported to the quiz platform on LearningMall at XJTLU.
Reflections on the AI Integration Practice
Despite the benefits that AI has brought to the quiz creation processes, teachers should be mindful of a few challenges or limitations regarding the AI integration practice. The first is related to prompt design and the AI generated questions. The author’s initial testing of the prompts and responses has found that more dialogues between the human teacher and AI are expected to improve the responses. Secondly, there are also concerns about the reliability, validity and accuracy of the quiz items generated by AI. During the AI-assisted quiz creation processes, there have been instances of unsuccessful distractors and irrelevance, for example, mismatches between key terms and definitions occurred from time to time. This echoes with the warnings from literature, such as the “possibility of errors” or “inaccurate information” (Elsen-Rooney, 2023, cited in Koraishi, 2023, p.70). The following two quotes serve to remind educators of the challenges while attempting to integrate AI into language education: Firstly, “AI models may not always produce correct or appropriate responses, leading to potential errors or misunderstandings in language learning” (Yang et al, 2020, cited in Özdere, 2023, P.157). Secondly, “Chat GPT is not a perfect system and requires teachers’ involvement and feedback…” There are “limitations such as making up information seemingly out of thin air with accompanying fake sources” (Koraishi, 2023, p.69).
Hence, while integrating AI into the creation of online quizzes, it is recommended that certain critical roles should be played by teachers (Koraishi, 2023), including to improve the design of AI prompts and skillfulness to format the various types of quiz items, to incorporate human input and oversight to ensure the accuracy and reliability of online quizzes assisted by AI (Owan, et. al., 2023), and to collaborate with subject teachers to proofread the quiz questions and ensure the alignment of quiz items with the intended learning outcomes.
Conclusion
The current case study describes how an EAP lecturer used AI technology to support language learning for the Degree Preparation Module titled “Trend in Marketing and Information Management”. It highlights an innovative educational practice involving the use of AI technology to facilitate quiz creation process, utilizing a learning management system for automatic grading and students’ performance monitoring, and employing online quizzes to offer immediate feedback and encourage active learning.
This article could be valuable for EAP practitioners seeking more efficient methods to create language support materials when offering institutional ELT support to departmental programs within EMI contexts. However, it is important to note that limitations such as the potential inaccuracies still necessitate teachers’ active involvement in the design, evaluation, and revision of AI-generated teaching and assessment materials. It is recommended that EAP lecturers integrate AI technology with human expertise and collaborate with subject area lecturers to ensure that the generated materials align with the intended pedagogical goals and effectively meet learners’ needs. It is expected that through ongoing exploration and improvement of AI-assisted practices, university educators can utilize these technological tools to provide comprehensive and engaging language support in EMI programs, thereby more effectively prepare students for their academic journeys.
Reference
Cohen, D. & Sasson, I. 2016. Online Quizzes in a Virtual Learning Environment as a Tool for Formative Assessment. Journal of Technology and Science Education, 6, 188-208.
Koraishi, O. 2023. Teaching English in the Age of AI: Embracing ChatGPT to Optimize EFL Materials and Assessment. Language Education & Technology, (2791-7010), 3, 55-72.
Luo, J. & Garner, M. 2017. The challenges and opportunities for English teachers in teaching ESP in China. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 8, 81-86-86.
Owan, V. J., et. al. 2023. Exploring the potential of artificial intelligence tools in educational measurement and assessment. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education, 19, 1-15.
Özdere, M. 2023. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in English Education: Opportunities and Challenges. Language Education & Technology, (2791-7010), 3, 137-172.
Paturusi, S., Chisaki, Y. & Usagawa, T. Development and evaluation of online quizzes to enhance learning performance: A survey of student assessment through MOODLE in Indonesian National University. Proceedings of International Conference on Information, Communication Technology and System (ICTS) 2014, Information, Communication Technology and System (ICTS), 2014 International Conference on, 2014. IEEE, 211-216.
Slamet, J. & Mukminatien, N. 2024. Developing an Online Formative Assessment Instrument for Listening Skill through LMS. LEARN Journal: Language Education and Acquisition Research Network, 17, 188-211.