It is important for students to conduct thorough preparation for their assessments, which involves a comprehensive understanding of the assessment tasks, practice and receive feedback for improvement. Meanwhile, teachers can facilitate this process by using XIPU AI to generate tailored content and help students prepare for various types of assessments across different academic disciplines. Alternatively, students can be trained to obtain the necessary skills to use XIPU AI independently for the same purpose. This article will take EAP (English for Academic Purposes) assessments as examples to demonstrate how XIPU AI can be applied specifically.
Task sheet comprehension check
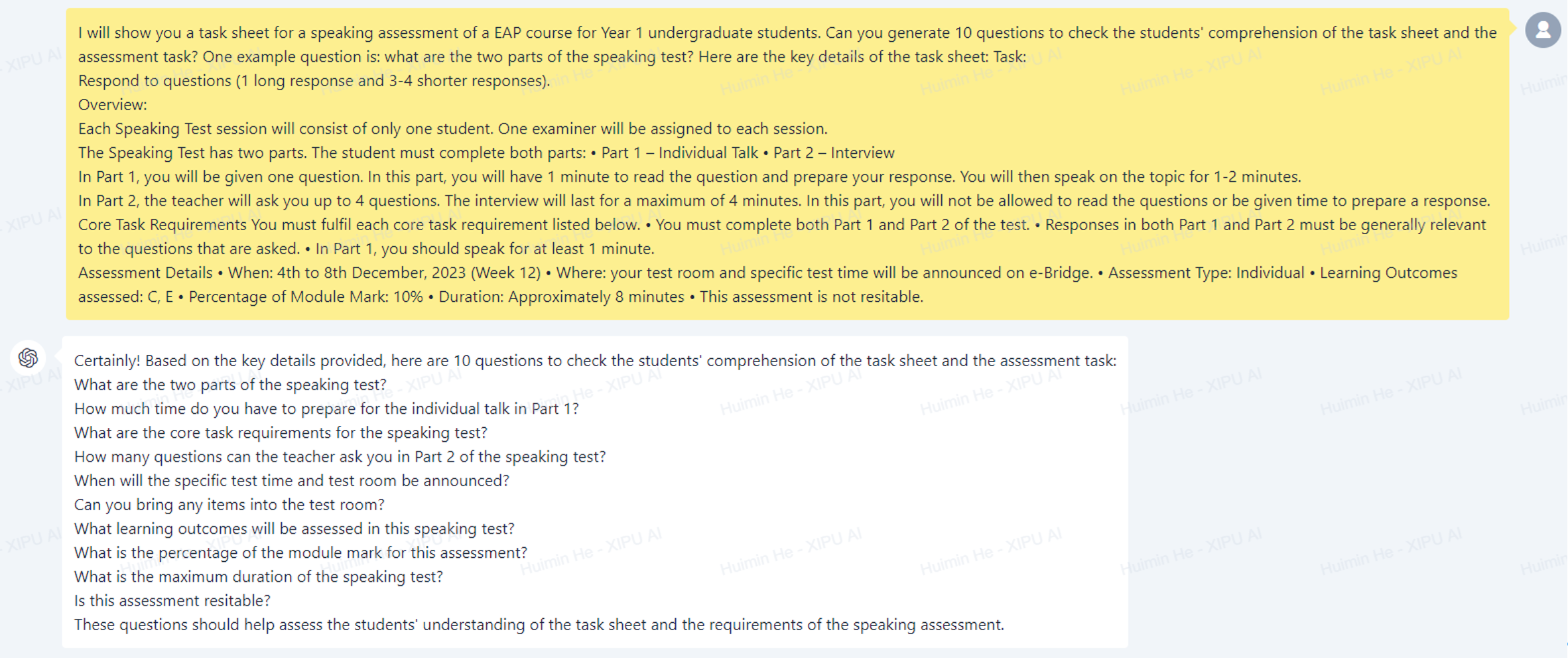
Students are usually provided with a task sheet about the assessments outlining the essential details, such as time and dates, core requirements, question types and exam format. Without a thorough understanding of the task sheet, students may fail to meet the criteria or perform well in the assessment. Therefore, it is vital for teachers to ensure students' comprehension of the assessment task and furnish them with appropriate feedback. Traditionally, teachers will manually craft questions for comprehension-checking and prepare the answers, which, however, is time-consuming and may likely miss some of the critical information in the sheet. On the other hand, with XIPU AI, we can expedite this process by simply copying and pasting the task sheet and writing a prompt to generate comprehension-checking questions and corresponding answers, aligning closely with the task sheet’s content (see the screenshot below). After that, these questions can be used for in-class group discussions or on interactive educational platforms such as Kahoot and Mentimeter. This facilitates the evaluation and deepening of students’ understanding of the assessments.
Practice questions and sample answers
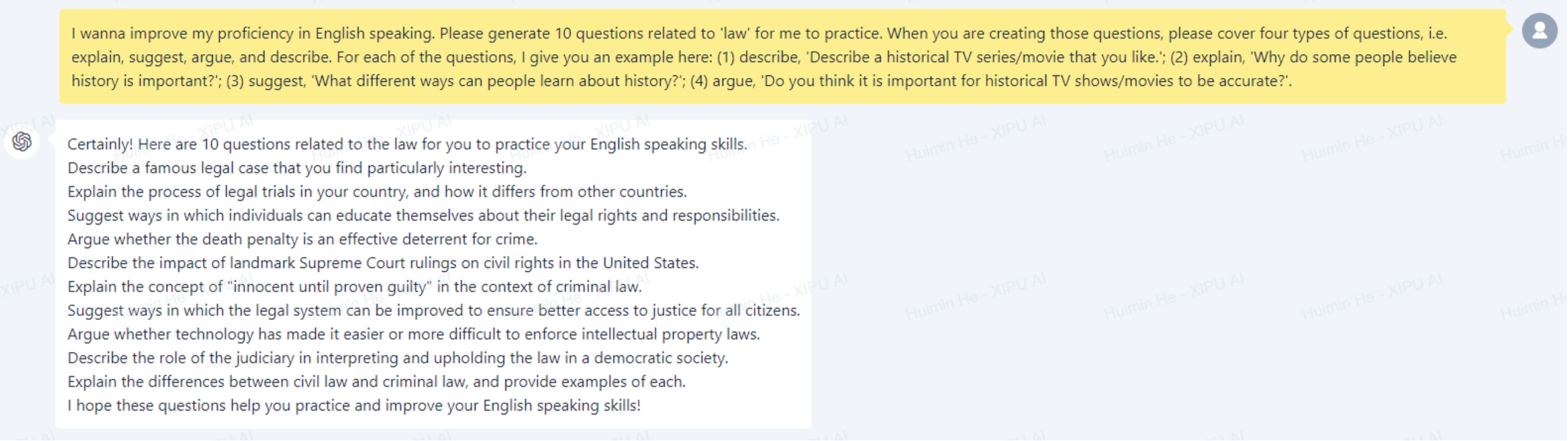
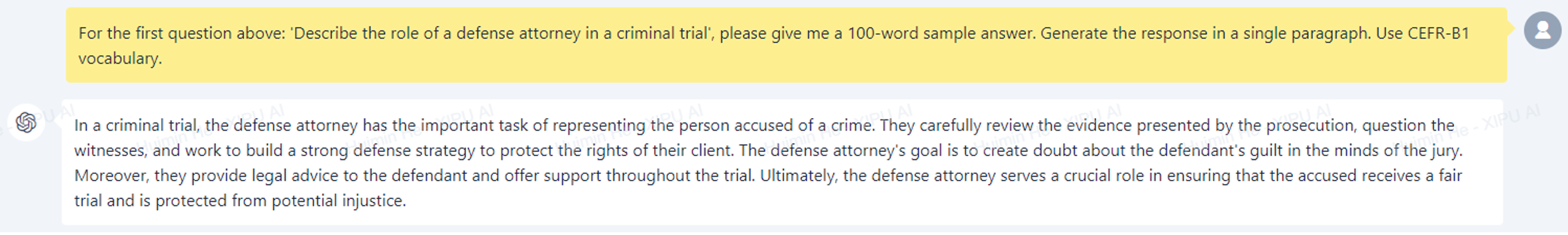
To effectively prepare for an assessment, students need to practice more on the particular question types or topics that are expected to appear in the actual assessment. For example, when preparing for a math exam, it is advisable for students to tackle a variety of practice questions. This approach helps them review the related concepts and get familiar with the question formats and methods of solving the questions. Moreover, access to sample answers to the practice questions is necessary for the students to self-check and reflect on their understanding. Given that many students may encounter difficulties accessing sufficient practice questions appropriate to their level, it would be beneficial to use XIPU AI to bulk-generate practice questions and sample answers for students to prepare for their assessments independently. In the context of Year 1 EAP speaking exam preparation, many sets of practice questions and corresponding sample answers have been produced using XIPU AI (see the screenshots below), and these materials fit with the question types, topics, student levels and learning outcomes of the EAP course.
Providing scaffolds for practice
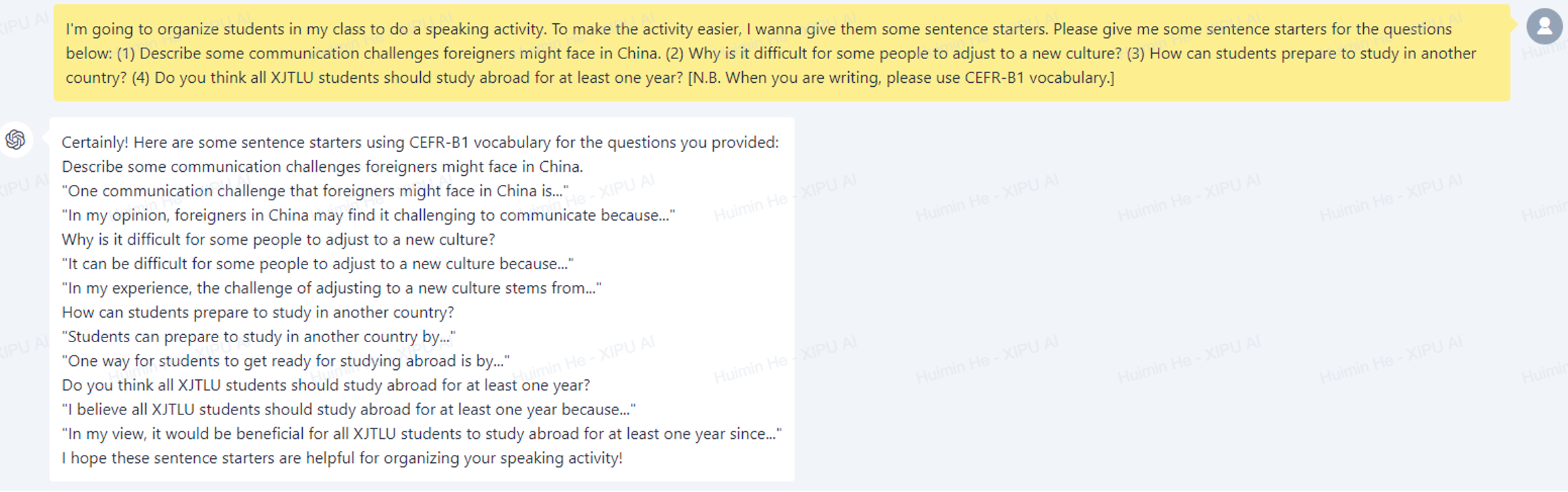
In the field of education, scaffolding encompasses a range of teaching methods aimed at guiding students step by step towards a deeper comprehension and, ultimately, increased autonomy in their learning journey. In addition to directly providing students with practice questions and sample answers, some scaffolds could be presented to help students answer the questions. This could be particularly helpful for lower-level students who need more assistance to comprehend and respond to the questions before they are able to handle the AI-generated practice questions independently. Furthermore, the scaffolds can be a key aspect of the learning outcomes, and in this way, students are only required to focus on understanding the key concepts rather than memorizing the format. For example, for a physics or maths practice question, useful formulas could be provided to assist students in completing the question. Similarly, for a linguistics course essay, some significant linguistics theories and essay structures could be shown to students along with the essay prompt. However, it can be time-consuming and less comprehensive if the scaffolds are manually produced by teachers, especially when dealing with a large number of practice questions and there may be various possible hints for each question. To demonstrate how XIPU AI can address this challenge, I will use the interview question types in the EAP speaking assessments. In order to help students with a lower level of English language proficiency to answer the practice questions generated by XIPU AI, I instructed XIPU AI to create a range of sentence starters (see the screenshot below), which students can use to start answering the questions. This not only assists and motivates the students to answer the questions but also reminds them to use the cohesive devices or signpost language included in the provided sentence starters to enhance the cohesion of their speech.
Addressing the diverse student needs
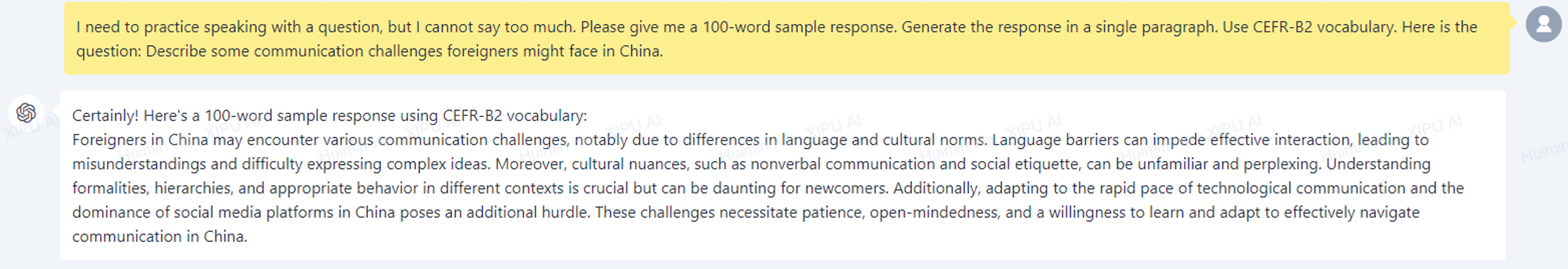
Students’ needs may vary due to individual differences in various factors, such as skills, abilities, knowledge, family and community background, and life experiences. This could be even more obvious among students enrolled in a relatively big class, where they may exhibit a range of needs in pursuit of their assessment objectives. For example, advanced students may want to practice on more complicated questions or areas of knowledge, while lower-level students may need support understanding such questions or knowledge and producing responses as shown in the advanced models. Furthermore, even in the same class, students may perceive the difficulties of a specific concept or practice differently, and thus, they may need to practice for different purposes. Using XIPU AI can effectively address different students' needs regarding assessment preparation. Teachers can obtain different sets of practice questions catering to diverse needs by simply indicating the suitable proficiency level or stating the focus of the questions. In the screenshot below, a prompt that suggests the student level (i.e., CEFR B2) was made to generate practice questions and sample answers suitable for students comfortable with challenges at this level. Although students were placed based on their language proficiency upon entering the EAP course, variations in proficiency levels still persist within the class. As such, preferences about the difficulties of practice questions, topics and sample answers may vary among students. Therefore, by just adjusting the student level in the prompt, teachers can get multiple sets of questions and answers within seconds, optimizing time efficiency and meeting individual student needs. Alternatively, students can be distributed with easier questions at the start of a semester and more difficult ones at the end of the semester, which reflects the learning progress of students.
Reflection and conclusion
To conclude, using XIPU AI to prepare students for assessments can be efficient and comprehensive. It can apply taught knowledge to generate what the students need for reviewing. The use of the content generated by XIPU AI can motivate students to prepare independently and effectively for their assessments. To maximize the benefits of XIPU AI, teachers should consider more factors in order to craft a clear and specific prompt. For example, a prompt should include the description of a context or activity, the role of XIPU AI, target group and outcome specifications. Furthermore, providing XIPU AI with specific examples of the desired output can help minimize the risk of misinterpretation. These examples could be taken from the available teaching resources such as textbooks, in-house workbooks and assessment materials. Lastly, the decision on whether or to what extent the XIPU AI-generated content would be used in practice should be made after teachers’ careful quality assurance based on their academic judgment, regarding the module specifications and student needs.







